 |
| Sinusitis |
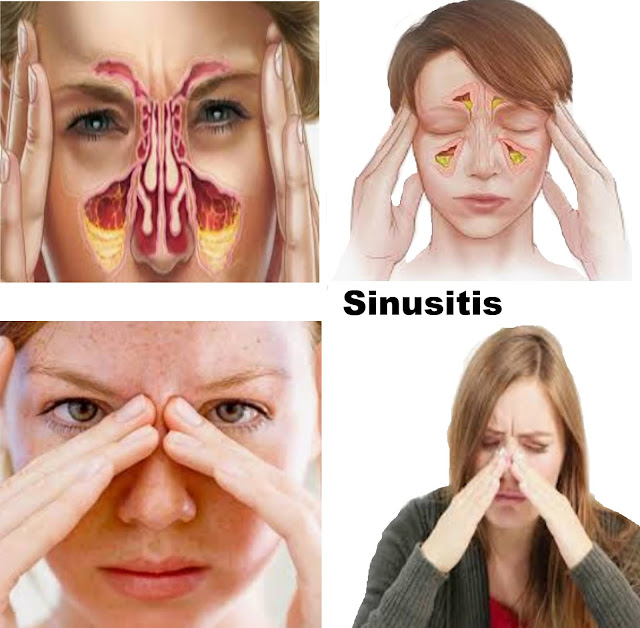
Sinusitis:
The
air cavities inside the bones around the nose and eyes are called sinuses. When
these sinuses become inflamed it is called sinusitis. The main sinuses are in
pairs. There are two frontal sinuses on either side of the forehead, two
maxillary sinuses under the eyes, the sphenoidal, and ethmoidal sinuses in the
skull. The sinuses have connections to the middle ear and nose. Their main
functions are: to keep the air in the middle of the nose warm and moist, to
keep the head light, to protect various organs of the brain, to control the
tone of voice and throat, to maintain body balance, etc. Inflammation of the
sinuses can cause runny nose and headaches. There may be pus in the sinuses,
there may be tumors, etc.
Types
of sinusitis:
There
are different types of sinusitis and they are discussed below:
Acute
sinusitis:
In this case, the illness usually lasts for 7 to 10 days. It can be intense and
mild in symptoms.
Recurrent
acute sinusitis:
It
lasts four times a year or more.
Sub-acute
sinusitis:
The
inflammation usually lasts for more than 4 weeks or 12 weeks.
Chronic
sinusitis:
It
lasts for more than 12 weeks.
Maxillary
sinusitis:
Infection
of the inner sinus called maxillary around the forehead or cheek is called
maxillary sinusitis. Teeth and headaches occur when it is infected.
Frontal
sinusitis:
Frontal
sinusitis occurs when there is inflammation of the frontal sinuses on the eyes
or in the bones of the forehead. The result is headaches.
Ethmoid
sinusitis:
Infection
of the ethmoidal sinus located between the two eyes causes pain and pressure in
the affected area, it is called ethmoid or ethmoidal sinusitis.
Sphenoidal
sinusitis:
Inflammation
of the butterfly-shaped sinuses on the inner palate of the mouth causes
sphenoidal sinusitis. When it is infected, pain is felt in the eyes and inside
the eyes and the pain spread to the palms of the head.
Symptoms:
The
most frequently seen symptoms in people with sinusitis are:
- Fever.
- Cough, which gets worse at night.
- Pain in the front of the head.
- Toothache.
- Nasal congestion.
- White, yellow or green streaks from the nose.
- Decreased sense of taste and smell.
- Pain and swelling in different parts of the eyes, nose, cheeks, and forehead.
- Bad breath.
Other
symptoms of sinusitis include:
- Nausea.
- A feeling of excessive fatigue or exhaustion.
- Moderate to severe discomfort in the chest.
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the upper jaw.
- Ear pain.
Sinusitis
test:
- X-rays of the nose show paranasal sinus problems, nasal congestion,
- Routine blood tests,
- Allergy test,
- Chest x-ray,
- Routine examination of urine,
- Blood sugar test,
- ECG
These
tests help a physician to diagnose sinusitis due to a bacterial, viral, fungal,
or other allergic reactions.
Prevention:
- Stay away from allergies and dust
- Need to use handkerchief or mask
- Smoking should be avoided
- The surrounding environment should be kept as clean as possible and kept clean and tidy
- Teeth need to be protected from tooth decay and other perishable substances
- Drink plenty of water.
Treatment
of sinusitis:
Proper
treatment is important for sinusitis. The medical procedures for sinusitis are
as follows:
Antihistamine
drugs:
These
drugs help to treat the symptoms of an allergic reaction. These prevent
inflammation of the sinuses and nasal cavity.
Nasal
decongestant spray:
These
can be effective if used for a short period of three to four days. This helps to flush out the accumulated fluid from the sinuses. Long-term use of these can
lead to dependence in which the nasal passages will become blocked due to
swelling and mucus if decongestants are not used.
Nasal
Saline Irrigation:
Rinse
your nasal passages using pure or saline water and clear the mucus secretion.
Topical
nasal corticosteroids:
These are prescribed to treat inflammation. The usual dose of these drugs can be used for a long time without any side effects or addictions.
Antibiotics:
It
is not a commonly used therapy for sinusitis because 98% of acute sinusitis
infections are caused by viruses or germs. Antibiotics are the primary
treatment for bacterial sinus infections. These do not provide any relief from
the symptoms, for which antibiotic treatment as well as medications without
other prescriptions are essential. Since antibiotic resistance has increased,
antibiotics are usually prescribed when symptoms last more than 7 to 10 days.
Surgery:
This
is the last resort when all the drugs have failed. It is usually needed in
cases of skeletal defects and is performed by an otolaryngologist. Surgery can
help correct defects in the lining of the nose, remove abnormal tissue growths
in the nose, and open closed passages. Depending on the condition, it may be
performed under local anesthesia.




0 Comments