 |
| Stroke |
Stroke
:
Oxygen-rich
blood circulation is needed in every cell of our body, even brain cells, to
survive healthy. If for some reason the blood vessels in the brain narrow or
become blocked, the brain cells become dull. This is what doctors call a
stroke.
Causes
of stroke:
- People with higher blood cholesterol levels are more likely to have a stroke.
- High blood pressure is the main cause of blockage of blood flow to the brain. Especially uncontrolled blood pressure increases the risk of stroke.
- There are other psychological problems, including stress and depression, but these problems are more likely.
- Those who sit and work all day. The risk of this disease is higher than others as there is no physical labour including walking.
- Eating more fried, fast food instead of nutritious food increases the risk of stroke.
- Smoking increases the risk of stroke along with many other illnesses.
- Regular excessive drinking increases the risk of stroke.
- People who suffer from diabetes and do not diet or exercise to control it are also more likely to have a stroke.
- Having heart disease increases the risk of brain stroke.
Symptoms
of stroke :
- Feeling numb or weak or paralyzed anywhere or part of the body. Numbness of the right or left side of the legs, arms, mouth or body, feeling weak in both legs.
- Inability to move, loss of balance in movement, inconsistency in the activities of various organs.
- Having trouble speaking, falling into a state of confusion, getting involved, blurring and not being able to speak or understand at all.
- Transient blurred vision or blurred vision in one or both eyes or no vision at all.
- Sudden onset of severe headache, dizziness, suddenly stunned for a while, nausea or vomiting.
- Severe symptoms of a stroke include fainting, convulsions, severe headaches and vomiting.
Types
of stroke:
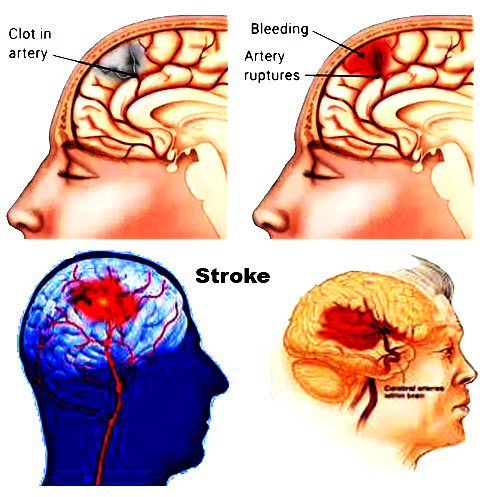
There
are two main types of stroke:
- Ischemic strokes and
- Haemorrhagic strokes
These
affect the brain differently and may be due to different reasons.
It is the most common stroke. This is because blood or oxygen cannot get to the brain due to blood clots in the arteries. Blood clots form when the arteries become narrow or when a type of fatty deposit called Plaque slowly blocks the arteries. As we age, the arteries begin to narrow on their own. But for some reason the speed of its occurrence increases drastically. These are:
- To smoke
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- High cholesterol level
- Diabetes
- Drinking alcohol
It
is less than ischaemic strokes. This happens when an artery in the head bursts
and bleeds into the brain or around the brain. Arterial bursts are usually
caused by high blood pressure. High blood pressure weakens the arteries of the
brain and increases the chances of bursts. Reasons for high blood pressure:
- Obesity
- Drinking alcohol
- To smoke
- Do not exercise
- Stress, which causes blood pressure to rise for some time
Stroke diagnosis:
Here
are some ways to tell if you have had a stroke:
- Physical measurements: Blood pressure measured, blood cholesterol measured, diabetes measured, amino acid measured
- Ultrasound: Looking at a picture of a cervical artery to see if the blood vessels are narrowing or closing.
- Arteriography: An x-ray of a type of dye inserted into a blood vessel that provides a picture of blood flow.
- CT scan (Computerized Tomography scan): 3D scan of the brain can be done
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An attempt is made to create a magnetic field to see if any part of the brain tissue has been damaged.
- Echocardiography: Echocardiography uses ultrasound to take a picture of the heart to see if any blood clots, bubbles or anything else is stopping the flow of blood.
What
to do to prevent stroke:
- Lose weight. Eat a balanced diet. Include adequate amounts of vegetables and fruits in your diet.
- Walk briskly for half an hour at least five days a week. Exercise hard in the sails. Sweat.
- You have to quit smoking.
- You need to sleep at least 5-6 hours every day. If it is less then various problems will occur.
- If you have blood pressure and sugar, you have to control it according to the rules.
- The belly should not be allowed to grow. Diet and exercise should be controlled.
- Care should be taken while exercising so that it does not become too hard or tiring.
- If you suddenly feel numb, numb, or have difficulty seeing or speaking or have difficulty swallowing, seek medical attention immediately without any risk.
Stroke
treatment:
Proper
treatment reduces the long-term problems from stroke. Specific treatment will
depend on the type of stroke. Several types of medications are usually given as
treatment. However, in some cases, surgery may be needed to remove the blood
from the brain and repair the burst artery. This surgery will cut your skull to
repair the burst artery and make sure that there is no blood clots anywhere.
Artificial metal plates will then be placed in place of the cut bones of the
skull. In addition, if there is a problem in swallowing, feeding with a tube,
giving fluid directly to the veins if there is a lack of water in the body,
giving oxygen with a face mask if there is a lack of oxygen in the blood, etc.
can be treated.




0 Comments