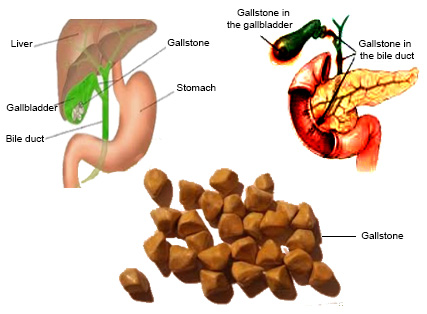
 |
| Gallstone |
Gallstones:
The gallbladder is on the
right side of the lower abdomen and it is pear shaped. Gallstones are hardened
stones that accumulate calcium and other salts inside the gallbladder. For some
reason, bile clots form in the gallbladder or bile duct and form a stone called
gallstones. This disease can occur if there is any problem in the bile duct.
Usually this disease is not due to any other reason. The size and type of
gallstones in the gallbladder are different. It can be small to medium round,
white, black, green etc. It can be like a grain of sand or the size of a
pigeon's egg. One or more stones can cause pain in the gallbladder. Currently,
the number of patients with this disease is a lot. As long as the stone is
bound to the gallbladder, the patient does not feel much discomfort, sometimes
a slight pain. But when this stone from the gallbladder enters the bile duct,
it causes unbearable pain and the patient becomes restless. This pain is called
biliary colic.
Causes of gallstones:
Bile secreted by the liver helps
to digest food. The main reason for the formation of gallstones is the
imbalance of water and fat content in the bile juice. Someone with hemolytic
anemia or thalassemia also has a tendency to form gallbladder stone. The bile
duct, which is stored from the gallbladder, flows gradually through the bile
duct to the first part of the small intestine or duodenum. This bile flow can
be disrupted due to food poisoning or inflammation of the gallbladder cells or
bile ducts, as a result bile clots and gradually form bile stones. If the
gallstones are small or like sand grains, they often come out on their own and
it is not clear when they come out. However, if the gallstones are large in
size and cannot be excreted, then pain occurs and the patient suffers. The
occasional pain symptom in the gallbladder area can often be seen. Gallstones
remain in the gallbladder cells for the rest of their lives and the patient
does not feel any pain. With this disease, bile secretion cannot be normal.
This disease can be caused due to constant mental work at home, taking
stimulant food like fish, meat etc., eating too much lime or any mechanical
disturbance. The patient does not feel anything as long as the stone is in the
gallbladder, sometimes there is a slight pain but only when the stone comes out
of the gallbladder into the bile duct. Then suddenly there is severe pain in
that place and the patient becomes restless with pain. Some gallstones are
caused by calcium salts or bilirubin but are more likely to be caused by bilirubin,
in very rare cases by calcium salts. This stone can be caused by excessive
production of bilirubin due to hemolysis. Too much bilirubin is the main reason
for the formation of pigment stones. If the bile flow is not proper, it is
known that the stones formed by the bile coagulation. Excessive cholesterol in
the bile can cause cholesterol stones. If there is excessive cholesterol in the
bile, it does not eventually break down and becomes hard to form stones.
In which case it is seen
more:
- If you are on an empty stomach for a long time, you are more likely to have gallstones.
- If you are overweight.
- Eating extra fat containing food.
- Suddenly lose weight in a short time.
- Men over 50 and women are more likely. to have gallbladder stones
- Pregnant women are more likely to have gallbladder stones.
- If someone in the family has gallstones, then others in the family also have a tendency to have this problem.
- If you have liver cirrhosis.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs and contraceptive pills can cause stones.
Symptoms of gallstones:
- Severe pain spreads from the right caucasus and the patient becomes restless and restless.
- Many times vomiting with pain, bile vomiting.
- Cold sweats occur with pain. The pulse is weak, there is a feeling of restlessness and coldness,there is difficulty in breathing.
- In many cases the patient has jaundice and the body turns yellow.
- Many times the pain lasts for 2/3 days then the pain subsides. When the pain subsides, it is important to understand that the stone has returned to the bile cells or is moving through the bile duct into the duodenum of the small intestine. In the case of duodenum, it often goes out with the stool and in some cases, it may require surgery.
- When the stone begins to pass through the gallbladder, it causes severe pain and the pain spreads around the abdomen.
Gallstones test:
The doctor will evaluate the
symptoms and then recommend a CT scan or ultrasound to look for stones. Test
liver function to check the health of the liver and gallbladder. X-rays are
used to check the obstruction of a bile duct using a special pigment flow
through the duct. Blood tests also help to check for complications and
infections.
Treatment of gallstones:
If the size of the stone is less
than15 mm, if it is not seen on X-ray, if the patient is moderately obese and
if the patient's symptoms are mild, bile acids like ursodeoxycholic acid should
be taken orally in the long run. It breaks down the rock and dissolves it.
Again the treatment is done through surgery. Cholecystectomy is the removal of
the gallbladder through surgery. This is done in two ways;through abdominal
incision and laparoscopy. Laparoscopy has some additional benefits such as no
need to cut the abdomen, the patient does not have to stay in the hospital for
a long time, the wound dries quickly, etc. One of the disadvantages is that if
there is a stone in the common bile duct, it cannot be removed.




0 Comments