 |
| Heart attack. |
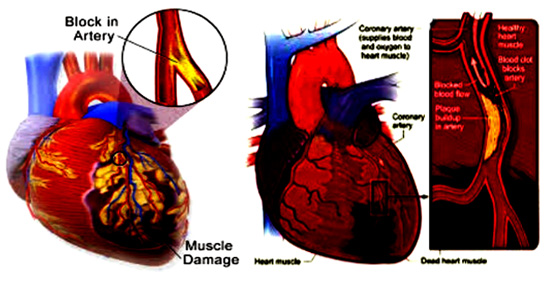
Heart attack:
The heart supplies blood
throughout the body. The heart has two small arteries called coronary arteries.
Cholesterol buildup in these coronary arteries interferes with arterial blood
flow, causing blood shortage in the heart and disrupting the supply of oxygen
that lead to heart attack or myocardial infarction. By beating about 72 times
per minute, the heart pumps blood throughout the body. When the work of this
heart is interrupted, it brings harm to the whole body. When someone fall in
heart attack feels like a sharp pain in the chest and this pain can last for
about 20 to 30 minutes. In many cases, the patient dies before reaching the
hospital. Failure to act promptly during a heart attack can result in death.
Again many times the patient feels chest pain and it can be cured after some
time.
Causes of heart attack:
Saturated fats accumulate in the
coronary arteries of the heart and thicken the artery wall.It prevents to flow
blood easily and causes blood clotting.This is the cause of heart attack. The
most common causes of a heart attack are:
- If someone in the family has a heart attack, the risk of heart attack is much higher.
- Smoking, alcohol, etc. increase the risk of heart attack.
- Heart attack can be caused by diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia etc.
- Obesity or obesity due to lack of physical activity is a cause of heart attack.
- Eat a high-fat diet and eat less vegetables and fiber.
- As a result of excessive stress or unrest.
- As a result of taking birth control pills or any other hormone-regulating drugs.
Time of heart attack:
There is no definite time for a heart
attack. For example, it may be during sleep at night, it may be during rest, it
may be during heavy physical work, it may be due to mental anxiety, etc. In 60
percent of cases, a heart attack occurs during sleep and the patient never
wakes up. A heart attack can happen at any time.
Symptoms of a heart attack:
The most common symptoms of a heart attack are:
The most common symptoms of a heart attack are:
- There may be shortness of breath.
- May cause nausea or vomiting.
- There may be severe pain in the chest.
- Feel pressure, pain and heaviness in the chest.
- Choking or hiccough.
- The body may sweat profusely.
- There will be problems with digestion of food and may cause burning in the upper part of the stomach.
- Blurry vision, dark vision, etc. can be a problem.
- If a heart attack occurs, the patient may become unconscious.
What to do if you have a heart
attack:
- The affected person should be taken to the hospital immediately without a moment delay.
- In no case should the patient walk to the hospital on foot or by car.
- If a heart attack is confirmed, the patient may be given instant aspirin or warfarin to stop the blood clotting.
- Nitroglycerin should be sprayed under the tongue.
- The patient needs to be emotionally reassured.
- At least two person will go to the hospital with the patient. This can reduce the time to diagnose and start treatment.
What to do to prevent heart
attack:
The following activity can be done to prevent heart attack:
- Try to stay free from mental pressure or anxiety.
- Blood pressure should be controlled by regular blood pressure measurements and taking proper treatment.
- Diabetes should be tested regularly and keep it controlled.
- Refrained from smoking, alcohol, etc.
- Obesity or overweight needs to be controlled.
- Eating fatty foods should be reduced and blood cholesterol levels should be reduced.
- Vegetables, fruits should be eaten more.
- You need to walk, run or do any physical work regularly.
Treatment of heart attack:
The patient should be rushed to
the nearest hospital for treatment of heart attack. In such cases, adequate
lighting and ventilation should be provided before or during the
hospitalization of the patient. The patient should be given a nitrate tablet
under the tongue.
In case of hospital selection, it
is better to have a hospital with medical facilities for heart disease.
Admission to the hospital should ensure continuous treatment under the
supervision of a cardiologist.
After being taken to the
hospital, the doctor will start the treatment as per the need. If the doctor
thinks it is necessary, the patient may need to have an ECG, oxygen may be
needed, and intra-venous fluid or nitroglycerin may be given.
First the amount of block has to
be determined by angiogram. If the blockage is high and the medication does not
seem to resolve, angioplasty may be needed. In this case, the surgeon will put
a few micro rings on the narrowed artery as needed.
If you still have a heart attack,
you can have open heart surgery or bypass surgery if the doctor deems it
necessary. In this case, the surgeon can cut a vein from the leg and use it to
create a bypass road for normal blood flow through the problem part of the
artery.




0 Comments