Gout:
Gout is an inflammatory disease. This causes inflammation
by the accumulation of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals in the synovial
joint or its surrounding tissues. In general, men are 5 times more affected by
this disease than women. It is the most noticeable inflammatory arthritis in
men and older women. The disease usually affects men over the age of 30 and
women after menopause. Again it can be at the age of sixty or seventy. In
general, the risk of this disease increases with age and the level of uric acid
in the blood increases. The normal level of uric acid in the blood is 2.0-7.0
mg / dL for men and 2.0-6.0 mg / dL for women. Men have higher levels of uric
acid than women, but uric acid levels in the blood also increase with age and
weight.
Symptoms of gout:
The presence of gout in the early stages is not very
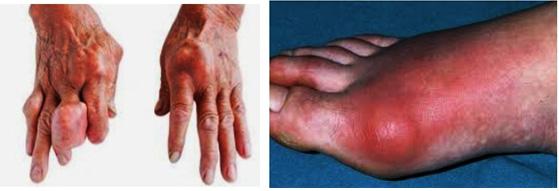
noticeable. Gout mainly affects the joints of the body. Symptoms usually appear
suddenly. The joints of the body become swollen, red and painful. It is more
common in the big toe or in the knee. It can also occur in the ankle joint,
middle foot joint, knee joint, small hand joint, wrist joint or elbow joint.
The main symptoms of gout are described below:
- Sudden onset of pain can be severe within 2 to 6 hours.
- Often the patient may wake up in the morning with severe pain. The pain may be accompanied by fever and fatigue.
- When the pain subsides, the affected area may become itchy and the skin may rise.
- The pain is so severe that the patient cannot wear socks, the affected joint becomes quite swollen and the skin becomes bright red.
- The pain gets better after 5 to 7 days.
- Some people are not infected again after being infected once and many may be infected again for the second time in a few years.
- If it is attacked for the second time in a year, then there is a possibility of getting chronic gout and there is a risk of joint damage.
- Sudden severe pain, even waking up due to pain.
- Swelling and redness of the big toe.
- Swelling of the knee, elbow or any other joint.
- Gradual bone and cartilage erosion.
- Gradually the joint may lose normal performance.
- Prolonged high levels of uric acid in the blood can lead to kidney stones.
- Crystals can accumulate in the joint and surrounding tissues to form tophus. Tophus can also cause sores, infections or pus.
Causes of gout:
Monosodium urate monohydrate crystals accumulate in the
joints due to increase in the amount of uric acid in the blood causing gout
disease. The reasons for the increase in the amount of uric acid in the blood
are as follows:
- Decreased renal excretion
- Increased reabsorption in the renal tubules.
- Renal failure.
- Lead poisoning.
- Lactic acidosis.
- Alcohol.
- Hyperketoacidemia.
- Diabetes insipidus.
- Barter syndrome.
- Thiazide and loop diuretics.
- Aspirin.
- Cyclosporine.
- Pyrazinamide.
- Increasing uric acid production.
- Myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative diseases.
- Psoriasis.
- Taking more fructose.
- Glycogen storage disease.
- Genetic disease lesch–nyhan syndrome.
- Chronic hemolytic anemia.
- Carcinoma and sarcoma.
- Cytotoxic drugs.
Diagnosis of gout:
Knowing the history of the disease, the patient can be
easily diagnosed by some physical examination and some laboratory tests. It is
very important to identify monosodium urate monohydrate crystals by doing some
routine blood tests, checking the level of uric acid in the blood and analyzing
the synovial fluid among the laboratory tests. In addition, X-ray of the
affected joint is also needed.
Prevention of gout:
Foods rich in vitamin C such as lemon, guava, mango,
orange ,amalaki, tomato, pineapple, raw pepper, fresh vegetables, cabbage, etc.
should be eaten in large quantities. Eating foods that have more purines should
be reduced such as different types of pulses especially lentils and peas,
beans, bean sprouts, asparagus, cauliflower, mushrooms, peas, spinach,etc. Red
meat such as beef, mutton, duck, rabbit, big bird or turkey, pigeon, partridge,
sheep, deer, brain, liver etc. Again various marine fish and fish eggs, shrimp,
crab etc. On the other hand, fruits and other vegetables should be eaten in
large quantities. Low purine rich foods such as milk and dairy foods, eggs,
lettuce, pasta, sago, flour, peanuts, etc. should be eaten.No irregularity can
be done in the name of dieting. If necessary, dieting should be done according
to expert advice. Eating more oily or spicy foods and more protein foods should
be reduced. Be careful about food. Foods that increase body fat or weight
should not be eaten at all or should be reduced. Drink plenty of water. This
will allow excess uric acid to be excreted from the body through urine and will
greatly reduce the chances of stones accumulating in the urinary tract.You have
to do light exercise every day according to the rules. If you exercise
regularly, you can stay safe from arthritis for a long time.Drugs that increase
uric acid levels such as thiazide diuretics, aspirin, niacin, etc. should be
avoided.Alcohol or any alcoholic food should not be eaten.
Treatment of gout:
First aid:
Apply ice to the affected joint and rest,Painkillers like
indomethacin, naproxen, ibuprofen, diclofenac, etc.,
colchicine,Glucocorticoids, intra-articular and systemic steroids,Joint aspiration,Inflammation
and interleukin-1.
Long-term treatment:
- If you are overweight, you have to reduce it,
- Alcohol should be avoided,
- Protein-rich foods such as seafood, poultry, sheep, pigeons, mutton, etc., eggs, bean sprouts, liver, etc. should be reduced as much as possible,
- Diuretics should be avoided if possible,
- Diseases that cause gout need to be treated appropriately,
- Allopurinol is commonly used medicine for long-term treatment,
- In addition, uricosuric agent probenecid is used to reduce uric acid levels in the blood;
Rehabilitation:
- Occupational therapy
- People with finger, wrist or hand joints may need a variety of adaptive equipment, such as jar openers, thick handle utensils, elastic shoe-laces, etc. to reduce pressure on the affected joint.
- ADL Joint Protection and Energy Conservation Training.
Physical therapy:
- Range of Motion, Stretching and Strengthening Exercises.
- Gait training.
- Orthosis.
- Modification.
- Use good quality right size shoes with cushions.




0 Comments