 |
|
kidney disease diagnosis.
|
In order to diagnose kidney disease, a health professional can use several tests.Test that helps to diagnose kidney diseases are below :
Urine Tests:
Different urine tests give important clues for the diagnosis of various types of kidney disease:
Routine urinalysis:
Routine urinalysis is a simple, inexpensive and very effective diagnostic test. It helps to find out abnormalities. Abnormality seen in a routine urinalysis gives important diagnostic clues where as a normal urinalysis does not provide enough clue for underlying kidney diseases.Presence of protein in urine which is known as proteinuria is seen in various kidney diseases. It should not be neglected. For chronic kidney disease the presence of protein in urine can be the first, the earliest and the only warning sign. Proteinuria is the first sign of diabetes involvement in kidney.Pus cells present in urine can indicate the presence of urinary tract infection.Protein and red blood cells present in urine provides diagnostic clues for inflammatory kidney disease such as glomerulonephritis.
Microalbuminuria:
Microalbuminuria test is an important urine test that measure the amount of albumin that is a protein is present in urine. This test provides the first and the earliest sign for the diagnosis of diabetes involvement in kidney. At this stage, the disease can be potentially reversible with proper treatment.
24 hour urine for protein test:
Patients with the presence of protein in urine, 24 hour urine for protein test is an important test to determine the total actual amount of protein lost in 24 hours. This test helps to assess the severity of the disease and also the effectiveness of treatment on the loss of protein.
Culture and sensitivity test:
This test helps to find out the type of bacteria causing urinary tract infections (UTI) and to select the appropriate antibiotic for its treatment. To get the final results of this test it may take 48-72 hours.
Urine test for acid fast bacilli:
This test is done to diagnose tuberculosis of urinary tract.
Different urine tests give important clues for the diagnosis of various types of kidney disease:
Routine urinalysis:
Routine urinalysis is a simple, inexpensive and very effective diagnostic test. It helps to find out abnormalities. Abnormality seen in a routine urinalysis gives important diagnostic clues where as a normal urinalysis does not provide enough clue for underlying kidney diseases.Presence of protein in urine which is known as proteinuria is seen in various kidney diseases. It should not be neglected. For chronic kidney disease the presence of protein in urine can be the first, the earliest and the only warning sign. Proteinuria is the first sign of diabetes involvement in kidney.Pus cells present in urine can indicate the presence of urinary tract infection.Protein and red blood cells present in urine provides diagnostic clues for inflammatory kidney disease such as glomerulonephritis.
Microalbuminuria:
Microalbuminuria test is an important urine test that measure the amount of albumin that is a protein is present in urine. This test provides the first and the earliest sign for the diagnosis of diabetes involvement in kidney. At this stage, the disease can be potentially reversible with proper treatment.
24 hour urine for protein test:
Patients with the presence of protein in urine, 24 hour urine for protein test is an important test to determine the total actual amount of protein lost in 24 hours. This test helps to assess the severity of the disease and also the effectiveness of treatment on the loss of protein.
Culture and sensitivity test:
This test helps to find out the type of bacteria causing urinary tract infections (UTI) and to select the appropriate antibiotic for its treatment. To get the final results of this test it may take 48-72 hours.
Urine test for acid fast bacilli:
This test is done to diagnose tuberculosis of urinary tract.
Urine volume measurement:
Urine output measurement is one of the simplest tests that help to identify kidney disease. Low urinary output can suggest kidney disease due to urinary blockage. This problem can create multiple illness or injuries.
Blood Tests:
Different types of blood test help to establish appropriate diagnosis of different kidney diseases:
Blood Tests:
Different types of blood test help to establish appropriate diagnosis of different kidney diseases:
 |
| kidney disease diagnosis. |
Blood test for eGFR:
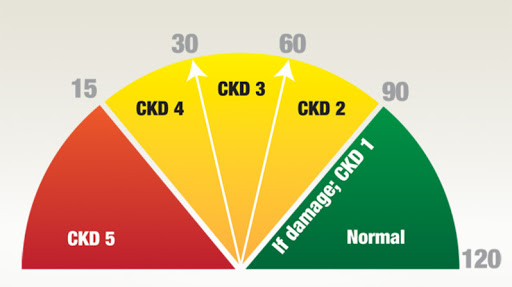
eGFR or estimated glomerular filtration rate helps to measure how well our kidneys filter waste from our blood. eGFR is a number based blood test for creatinine, which is a waste product in our blood. For normal good function kidneys, the eGFR value is greater than 90. eGFR value range 60 to 89 indicates a sign of kidney damage such as protein in the urine or physical damage to the kidneys. eGFR value range 30 to 59 indicate moderate kidney damage. eGFR value range 15 to 29 indicate severe kidney damage and eGFR value less than 15 indicate the kidneys are about to fail or already have failed.
Creatinine and Urea:
Creatinine and Urea levels of blood are two most important test for kidney that indicate the function of the kidneys. Creatinine and urea are two by- products in our blood which are normally removed from the blood by the kidney through urine. When the kidney does not function properly then creatinine and urea levels in blood increase. Normal range of serum creatinine value is 0.6 to 1.4 mg/dl and normal range of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) value is 20 to 40 mg/dl. Higher values of creatinine and urea indicate the kidney damage. Compared to blood urea nitrogen creatinine level is a more reliable guide of kidney function.
Hemoglobin:
Healthy kidney helps to produce red blood cells that contain hemoglobin. Low hemoglobin level in the blood causes anemia. Anemia is a important and common sign and symptoms of chronic kidney diseases. Anemia can also occur due to other illnesses.
Other blood tests:
Other blood tests that can be done for kidney patients are: blood sugar, serum albumin, cholesterol, triglyceride, WBC, electrolytes, calcium, phosphorous, bicarbonate etc.
Creatinine and Urea:
Creatinine and Urea levels of blood are two most important test for kidney that indicate the function of the kidneys. Creatinine and urea are two by- products in our blood which are normally removed from the blood by the kidney through urine. When the kidney does not function properly then creatinine and urea levels in blood increase. Normal range of serum creatinine value is 0.6 to 1.4 mg/dl and normal range of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) value is 20 to 40 mg/dl. Higher values of creatinine and urea indicate the kidney damage. Compared to blood urea nitrogen creatinine level is a more reliable guide of kidney function.
Hemoglobin:
Healthy kidney helps to produce red blood cells that contain hemoglobin. Low hemoglobin level in the blood causes anemia. Anemia is a important and common sign and symptoms of chronic kidney diseases. Anemia can also occur due to other illnesses.
Other blood tests:
Other blood tests that can be done for kidney patients are: blood sugar, serum albumin, cholesterol, triglyceride, WBC, electrolytes, calcium, phosphorous, bicarbonate etc.
Radiological Tests:
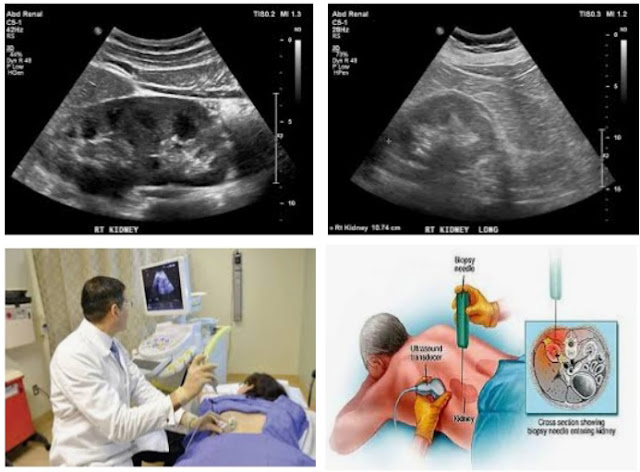
Ultrasound of the kidneys:
Ultrasound of the kidney is an effective test that helps to understand the size of the kidney,presence of stones,cysts and tumors in the kindney. An ultrasound also can also detect blockage to urine flow within the urinary tract. In advanced stage of CKD or ESKD both kidneys is also found to be small in size.
X-ray of abdomen:
This test is useul for the detection of calcium containg stones within the urinary tract system.
Intra venous urography:
Intra venous urograghy is a specialized X- ray test. During this test a radio opaque iodine containing dye is injected into a vein within the arm. This dye then passes through the kidney and gets excreted in to the urine. The urinary tract are rendered radio-opaque and this permits visualization of the whole urinary tract. A series of X-ray pictures are taken at specific time intervals which gives a comprehensive view of the anatomy of the urinary system. This test can reveal problems like stone, obstruction, tumor and abnormalities in structure and performance of the kidneys.
Voiding cystourethrogram:
Most commonly this test is used in the evaluation of urinary tract infection in children. During this special X - ray test, under sterile conditions, the bladder is filled with contrast medium via the urinary catheter. After the bladder is filled, urinary catheter is removed and therefore the patient is asked to urinate.This test is helpful to diagnose backflow of urine into the ureters and up to the kidneys. It also helps to identify structural abnormalities of urinary bladder and urethra.
Other radiological tests:
For the diagnosis of certain kidney diseases in special circumstances other tests like CT scan of kidney and urinary tract, renal doppler, radionuclear study, renal angiography, antegrade and retrograde pyelography etc. are often done.
Kidney Biopsy:
Kidney biopsy is a very important and effective test to diagnose of certain kidney diseases such as glomerulonephritis, tubulointerstitial diseases etc. During a kidney biopsy a tiny piece of kidney tissue is removed through a needle and examined under a microscope. When detailed history, physical examination and routine tests are unable to diagnose kidney diseases then a kidney biopsy may provide additional information which will help to diagnose accurately.This information helps a nephrologist to plan effective treatment strategy and guide patients and their family about the severity and course of the disease.Ultrasound or CT scan is done to detect the position of kidneys and to fix exact biopsy site. Kidney biopsy is done under anesthesia.With the help of a hollow biopsy needle 2 or 3 small thread like pieces are obtained from the kidney. These specimens are then sent to the pathologist for histopathology examination.In order to prevent bleeding after the biopsy pressure is applied to the biopsy site. The patient is placed on complete bed rest for 6-12 hours and discharged the following day.The patient is suggested to avoid heavy work or exercise for a minimum of 2-4 weeks after the biopsy procedure.
Ultrasound of the kidneys:
Ultrasound of the kidney is an effective test that helps to understand the size of the kidney,presence of stones,cysts and tumors in the kindney. An ultrasound also can also detect blockage to urine flow within the urinary tract. In advanced stage of CKD or ESKD both kidneys is also found to be small in size.
X-ray of abdomen:
This test is useul for the detection of calcium containg stones within the urinary tract system.
Intra venous urography:
Intra venous urograghy is a specialized X- ray test. During this test a radio opaque iodine containing dye is injected into a vein within the arm. This dye then passes through the kidney and gets excreted in to the urine. The urinary tract are rendered radio-opaque and this permits visualization of the whole urinary tract. A series of X-ray pictures are taken at specific time intervals which gives a comprehensive view of the anatomy of the urinary system. This test can reveal problems like stone, obstruction, tumor and abnormalities in structure and performance of the kidneys.
Voiding cystourethrogram:
Most commonly this test is used in the evaluation of urinary tract infection in children. During this special X - ray test, under sterile conditions, the bladder is filled with contrast medium via the urinary catheter. After the bladder is filled, urinary catheter is removed and therefore the patient is asked to urinate.This test is helpful to diagnose backflow of urine into the ureters and up to the kidneys. It also helps to identify structural abnormalities of urinary bladder and urethra.
Other radiological tests:
For the diagnosis of certain kidney diseases in special circumstances other tests like CT scan of kidney and urinary tract, renal doppler, radionuclear study, renal angiography, antegrade and retrograde pyelography etc. are often done.
Kidney Biopsy:
Kidney biopsy is a very important and effective test to diagnose of certain kidney diseases such as glomerulonephritis, tubulointerstitial diseases etc. During a kidney biopsy a tiny piece of kidney tissue is removed through a needle and examined under a microscope. When detailed history, physical examination and routine tests are unable to diagnose kidney diseases then a kidney biopsy may provide additional information which will help to diagnose accurately.This information helps a nephrologist to plan effective treatment strategy and guide patients and their family about the severity and course of the disease.Ultrasound or CT scan is done to detect the position of kidneys and to fix exact biopsy site. Kidney biopsy is done under anesthesia.With the help of a hollow biopsy needle 2 or 3 small thread like pieces are obtained from the kidney. These specimens are then sent to the pathologist for histopathology examination.In order to prevent bleeding after the biopsy pressure is applied to the biopsy site. The patient is placed on complete bed rest for 6-12 hours and discharged the following day.The patient is suggested to avoid heavy work or exercise for a minimum of 2-4 weeks after the biopsy procedure.




0 Comments