 |
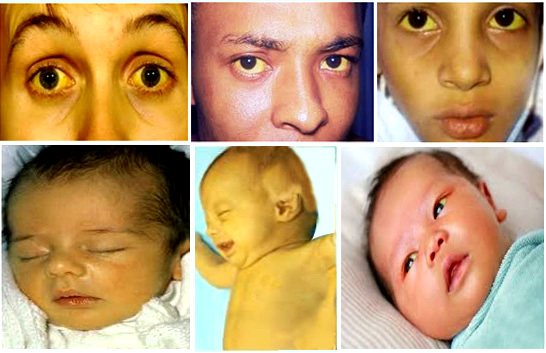
| Jaundice |
Jaundice:
Jaundice is a symptom of disease, it is not a
disease. Jaundice occurs when the levels of a type of pigment called bilirubinin the blood increase. The red blood cells break down normally to make
bilirubin, which is then processed in the liver and enters the digestive tract
through the bile ducts with the bile juice. Bilirubin is excreted from the body
through the bowel. Any inconsistency in this long cycle of bilirubin increases
bilirubin level in the blood and causes jaundice. In this disease the white
part of the eye becomes yellow. High levels of jaundice can cause yellowing of
the hands, feet, and even the body. In addition, the colour of the urine becomes
light to dark yellow. In most cases of jaundice, an important organ like the
liver is affected. And in some cases, it can be life-threatening.
Signs and symptoms of jaundice:
- The main symptom of jaundice is yellowing of the eyes and urine, and if the problem is severe, the whole body may turn dark yellow.
- Physical weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Feeling of fever or shivering with fever.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Mild or severe abdominal pain.
- Too often the toilet turns pale.
- Itchiness.
- Hardening of the liver.
Causes of jaundice:
Jaundice occurs when the level of bilirubin in the blood increases. Liver disease is usually the leading cause of jaundice. Everything we eat is processed in the liver. The liver can be diseased for a variety of reasons. Hepatitis A, B, C, D and E viruses cause inflammation in the liver which is called viral hepatitis. All over the world hepatitis viruses are the main cause of jaundice. Excessive alcohol consumption is one of the leading causes of jaundice in developed countries.
In addition, jaundice can be caused by autoimmune liver disease, hereditary causes and many other types of liver disease. Jaundice is also often caused by side effects of the drug. In addition, diseases such as thalassemia and haemoglobin E-disease can cause blood clots or jaundice if you have gallstones or tumours. Again, jaundice can be caused by cancer of the liver or elsewhere. It is not right to think that jaundice means liver disease.
Types of jaundice:
There are 3 main types of jaundice:
Hemolytic jaundice:
Red blood cells are one of the different types of blood cells. These blood cells break down and produce bilirubin as an end product. If for some reason the red blood cells break down more than normal, the level of bilirubin in the blood increases and jaundice occurs.
Hepatocellular jaundice:
This jaundice is usually caused by liver cell problems. Another of the many functions of the liver is to convert bilirubin into bile juice. The liver works as a factory, if there are any problems in the liver cells such as carcinoma of the liver, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, etc. then the liver cannot function normally, resulting in bilirubin can not convert into bile juice. Unable to do so, free bilirubin mixes with the blood and causes jaundice.
Obstructive jaundice:
After converting bilirubin into bile juice by the liver, it accumulates in the gallbladder. It then enters the duodenum byhepatopancreatic ampulla to digest fatty foods. If for some reason the produced bile juice cannot enter the duodenum normally or is obstructed, then jaundice that occurs is called obstructive jaundice. This type of jaundice is usually caused by gallbladder stones, bile duct stones, inflammation of the gallbladder, etc.
Diagnosis of jaundice:
Serum bilirubin test:
The normal level of serum bilirubin in the blood is 0.2 to 1.2 mg per deciliter. If the level of serum bilirubin in the blood is more than 3 mg per deciliter, it is called clinical jaundice and if it is less, it is called latent jaundice.
Ultrasonogram:
Ultrasonogram gives an idea of any structural abnormalities in the liver, gallbladder and biliary tract such as tumours, abscesses, tissue malformations, such as cirrhosis, presence of stones in gallbladder or blockage of bile ducts.
CT scanning:
Excellent reflections are obtained through CT scanning and clear idea about tumours in the liver, fatty liver, presence of other substances in the liver etc.
MRI:
It also provides a clear picture of the liver and makes the diagnosis easier.
X-ray:
A simple X-ray can easily determine if there are stones in the gallbladder.
Prevention of jaundice:
In order to prevent jaundice we can maintain the following options:
- Hepatitis A and E viruses are transmitted through food and water. So you have to eat pure food and drink pure water all the time.
- Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and Hepatitis D are contagious and spread these through blood, syringes and physical contact with the infected person. So We have to be conscious during blood taking, syringe using and physical contacting.
- Get hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines to stay free from the risk of getting hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- If you need to take blood in the body, you must do the necessary screening.
- Disposable syringes should be used.
- Refrain from drinking alcohol and taking drugs.
- Have safe sex.
- Stay away from chemicals emitted from mills.
- Be sure to use a new blade when saving at the salon.
- Jaundice can be a cause of death in many cases so be careful to avoid this disease.
Treatment of jaundice:
Adequate rest is very important for the treatment of viral hepatitis. In some cases, a hepatitis patient may need to be hospitalized. Viral hepatitis usually heals completely in 3 to 4 weeks. At this time pain medications such as paracetamol, aspirin, sleeping pills and any other unnecessary medications should not be taken. Morphine or sleeping pills should not be taken at this time. Alcohol addicts must refrain from consuming alcohol. In the case of jaundice, it is not advisable to take any medicine without the advice of a specialist.




0 Comments