 |
|
Treatment for kidney diseases.
|
Treatment for kidney disease depends on the type of kidney disease. Different type of kidney disease has a different type of treatment. Kidney disease is divided into 5 stages. Kidney disease or kidney failure treatment includes the following options:
Medications:
At first, find out the causes of kidney disease than try to stop or prevent or slow down the progression of kidney disease. If the causes are diabetes, high blood pressure, nephritis, kidney stone, polycystic kidney and urinary tract infections then we have to treat these causes to keep our kidney safe or healthy. Diabetes can be controlled by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. If necessary we can use some medicine or insulin to control diabetes. In order to lower cholesterol levels, we can use cholesterol reducing medicine that helps to lower high blood pressure. For anaemia, we can take an iron tablet, vitamin B or folic acid supplements. Other causes can be treated with proper medications. Kidney disease at an early stage can be cured with proper treatment. Medications help to solve the cause of kidney disease and keep them healthy and safe.
Changes in dietary and lifestyle:
When our kidney disease is at the primary stage then changes in dietary and lifestyle can help to keep our kidney healthy and safe. This includes the following options:
- Follow a diet chart that is prescribed by a doctor or nutritionist.
- Getting plenty of rest.
- Regular exercise.
- Avoid alcohol consumption that makes the kidneys to work harder.
- Limit to intake salt.
- Avoid smoking.
- Weight loss.
- keep fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains and low-fat dairy product on your daily menu.
- Avoid cholesterol-rich foods.
- When kidney disease reaches at the end stage of kidney completely failed to perform its duty properly. In this case, only two ways remain to us to save our life.
- Dialysis and
- Kidney transplantation.
Dialysis:
Dialysis is an artificial method to filter blood. It works as an artificial kidney. It is a temporary treatment for kidney failure patients. There are two types of dialysis:
Hemodialysis:
Hemodialysis simply knew as dialysis is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working properly. In hemodialysis, blood is pumped through a special machine that filters waste products and liquids. Hemodialysis is done at home or in a hospital or dialysis centre. Most people have three sessions per week, each lasting 3 to 5 hours. It can also be done in shorter sessions. Several weeks before the start of hemodialysis most people will have surgery to create an arteriovenous(AV) fistula. An AV fistula is usually formed by connecting an artery and vein just below the skin in one arm. Larger blood vessels allow an increased amount of blood to flow continuously through the body during hemodialysis treatment. This means more blood can be purified. An arterial graft (a looped, plastic tube) can be implanted and used for the same type if an artery and vein cannot be joined together. The most common side effect of hemodialysis is high blood pressure, muscle cramps and itching.
Peritoneal dialysis:
The peritoneum (the membrane that matches the abdominal wall) stands for the kidneys. A tube is implanted and used to fill the stomach with a liquid called dialysate. Blood waste products from the peritoneum flow into the dialysate. The dialysis is then expelled from the stomach.Where the
abdomen is full and dry most of the day and there is peritoneal dialysis
with the help of an uninterrupted cycle, The person sleeps at night
using a device to run fluid cycle in and out of the abdomen. The common
side effect of the peritoneal dialysis is an infection in the abdominal
cavity or the area where the tube was implanted. It also can causes
weight gain and hernias.
 |
|
Treatment for kidney diseases.
|
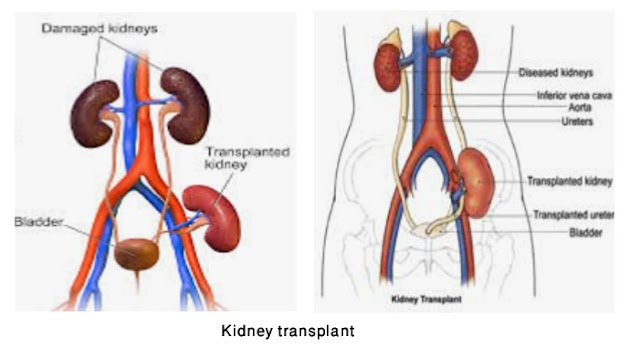
Kidney transplantation:
Kidney transplant is a surgical procedure to place a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor into a person whose kidneys are no longer function properly. For kidney transplant, living donor can be genetically related or non-related donor. Related or non-related donor is determined by biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. After receiving the new kidney the person will need to take medications to make sure that the body does not reject it. Transplant matching process is lengthy and everyone is not eligible for a transplant.




1 Comments
I want to use this opportunity to testify of the marvelous work of Dr. Isaac and how he has helped me in curing my sickness and bringing happiness into my life. I can really vouch for Dr. Isaac in herbal treatment. I was suffering from Cervical Cancer and infected with HPV 16. I used to have incessant bleeding and there was nothing I could do until a childhood friend introduced me to Dr. Isaac Remedies. I spoke with him and ordered his recommended medication which was delivered to me through DHL. Immediately I began using the herbal medicine, within 2 weeks I couldn't feel any pain. It took me 6 weeks to finish the medicine and afterwards I was completely cured. I highly recommend that you contact him to help you at his email drisaacherbscure2@gmail.com OR What'sApp/Call him at +234 8075449538.
ReplyDelete