 |
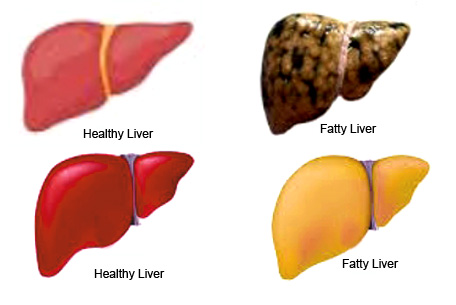
| Fatty liver. |
Fatty Liver Disease:
The liver is one of the biggest internal
organs in our body. It is the second biggest organ of the body. It helps in
digesting food and storing energy in our bodies. It helps process nutrients
from food and beverages and filters harmful substances from the blood. Fatty
liver occurs when a large amount of fat is made in the cells of the liver.
Although it is normal to have a very small amount of fat in these cells, the
liver is considered a fatty liver if it contains more than 5% fat. Fatty liver
is also widely known as hepatic steatosis. Too much fat in the liver can cause
inflammation of the liver which can damage the liver and create sores and
subsequently make the liver dysfunctional. This condition is called fatty liver
disease.
Symptoms of fatty liver:
There are several symptoms of fatty liver,
although all of them may not be present. Some symptoms of fatty liver:
- Fatigue and weakness,
- Slight pain or fullness in the right or center abdomen,
- Liver enzymes levels including AST and ALT will be high,
- High levels of insulin,
- High levels of triglyceride,
- Loss of appetite,
- Nausea and vomiting,
- Moderate to severe abdominal pain,
- Yellowing of skin and eyes,
- Weight loss,
- Bleeding through the nose,
- Itchy skin,
- Swelling in the abdomen,
- Swollen feet,
- Increased breast size in men than normal,
- Confusion.
Causes of fatty liver:
Many factors can cause a fatty liver. Some
causes are:
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with inflammation and stimulates the liver to store fat.
- Excess belly fat: People who have normal Bodyweight but carry too much fat around their Waist may develop fatty liver.
- Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance and high insulin levels can increase liver fat storage in people who are suffering from type-2 diabetes and metabolic disorder.
- Refined carbs intake: when overweight or insulin-resistant individuals consume high amounts of refined carbs or frequently intake refined carbs then it promotes liver fat storage.
- Consumption of sugary beverages: Sugar-sweetened beverages such as soda and energy drinks contain high fructose that drives liver fat accumulation.
- Impaired gut health: A study has shown that an imbalance in gut bacteria or other gut health issues can contribute to developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Other less common causes are:
- Pregnancy,
- Rapid weight loss,
- Some types of infection like hepatitis C,
- Exposure to the certain toxin,
- Side effects of some types of medications like amiodarone, tamoxifen, and valproic acid, etc.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Family medical history about any kind of liver disease.
- Alcohol consumption and other lifestyle habits.
- Medical conditions.
- Running medications.
- Recent health changes.
- Fatigue experience.
- loss of appetite, etc.
- Drink enough pure drinking water everyday.
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption.
- Keep your body weight healthy.
- Take medication that is recommended by your doctor.
- Keep a nutrient-rich diet on your daily menu that is low in trans fats, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates.
- Keep your blood sugar levels, triglyceride levels, and cholesterol levels control.
- If you have diabetes, follow the treatment plan that is recommended by your doctor.
- Exercise five days a week for at least 30 minutes every day.
- Keep more fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet. Avoid taking too much sugar and salt and choose whole grains instead of processed foods.
- Reduce saturated fat and trans fats and replace them with monosaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce the risk of heart diseases associated with NAFLD.
- Exercise regularly to control your weight and reduce the fat stored in the liver.
- If you take vitamin, or alternative herbal supplements, it is important to talk to your doctor and seek his advice. Some herbal medicines can cause damage to your liver.
- People with damaged liver are more prone to a few infections and pneumococcal disease. It is important that people with fatty liver get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B, the flu, and pneumococcal diseases. Hepatitis can be extremely dangerous for people with fatty liver and can even lead to liver failure.




1 Comments
Great post and thanks for sharing these prevention tips. To cure fatty liver problem taking herbal liver supplements is useful way.
ReplyDelete